Companies are about to enter their “blackout period,” where they are unable to repurchase their own shares
Trading in the U.S. stock market has been quiet of late, but the calm may not last for long.
Major U.S. companies are about to enter their “blackout” period, which will remove a steady—and perhaps underappreciated—factor that has been buttressing equity values.
A “blackout” period refers to how most companies and corporate insiders are prohibited from repurchasing their own shares in the month before the release of their quarterly results. Companies buying back their own stock have been providing a major floor to equity prices. According to Goldman Sachs, companies spent $384 billion on buybacks in the first half of the growth, an amount that represents growth of 48% from the prior year.
“Buybacks provide a tremendous amount of support to the market, and with blackout season coming, we won’t have that added measure of support,” said Scott Glasser, the co-chief investment officer of ClearBridge Investments, which has about $140 billion in assets.
Glasser spoke at last week’s Legg Mason Investment Forum, where he said equities were “overdue for a correction,” and that the blackout period could add to the odds of one occurring.
According to Goldman’s data, 18% of the companies in the S&P 500 index SPX, -0.56% are currently in their blackout period. This will rise to 86% by Oct. 5.
“Since 2000, S&P 500 returns have been comparable in blackout and non-blackout periods, but realized volatility has been nearly 1 point higher in blackout periods than when a majority of firms are free to repurchase stock (14.4 versus. 13.6),” the investment bank wrote in a note to clients.
If stocks do become volatile in the coming month, that wouldn’t mark the first time in 2018 that blackout periods have coincided with market declines. In fact, the issue was cited as being a contributing factor to selloffs in early February. At the time, Goldman wrote that blackout issue was “likely intensifying the decline” in the major averages, which resulted in corrections—or 10% declines from a peak—for both the Dow Jones Industrial Average DJIA, -0.35% and the S&P 500.
Vincent Deluard, global macro strategist at INTL FCStone, calculated that stocks that were in a blackout period during the worst of that selloff underperformed the market by 150 basis points, or 1.5%.
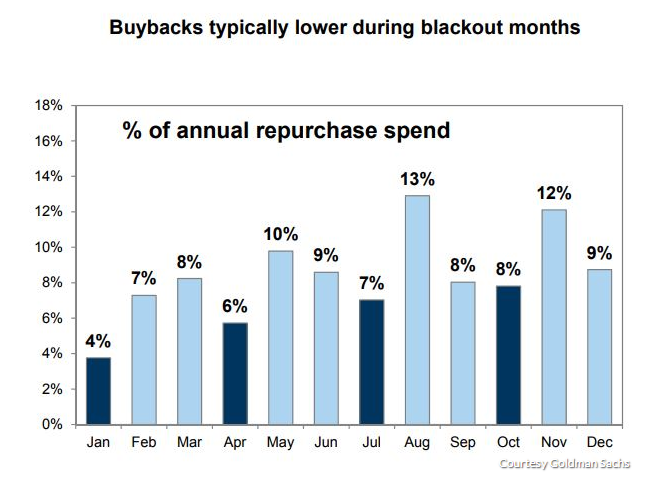
There are four blackout months a year, but as each company releases its results on its own set schedule, the blackout period won’t necessarily coincide with a calendar month. However, the concentration of results during the multiweek span that comprises the earnings season means that four months—January, April, July, and October—see this impact the most. On average, 6.25% of a company’s annual repurchasing expenditure is done in a blackout month, compared with 9.5% for non-blackout months and 8.4% overall.
Roughly 8% of a total year’s buyback spending is done in October, Goldman wrote.
If the blackout period does correspond with broad-market weakness, the impact will likely be concentrated within a few major stocks that have been doing the bulk of the buyback activity. Just 10 companies account for 78% of all buyback activity, while Apple Inc. AAPL, +0.24% alone accounts for 24%. Goldman expects stock repurchases will reach a record $1 trillion in 2018.
Despite questions about trade uncertainty and other factors, volatility has been extremely low on Wall Street of late. The S&P 500 hasn’t closed with a move of 1%—in either direction—since late June, and the benchmark index currently sits about 0.4% away from record levels. The Cboe Volatility Index is at 12.65, well below its long-term average between 19 and 20. While the so-called “fear index” is up nearly 15% for 2018—following an historically low year for volatility in 2017—it has dropped more than 20% since the start of the third quarter.

